A Step-by-Step Guide to Health Insurance Enrollment: Everything You Need to Know

Health insurance is more than just a policy—it’s a financial safety net that ensures you and your loved ones receive quality medical care without the burden of exorbitant costs. Whether you’re enrolling for the first time, switching plans, or renewing coverage, understanding the process is crucial to securing the best protection.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through health insurance enrollment, covering eligibility, key deadlines, required documents, and insider tips to avoid common mistakes. By the end, you’ll feel confident navigating the system and making informed decisions.
Why Enrolling in Health Insurance is Essential
Medical emergencies can strike unexpectedly, and without insurance, a single hospital visit could lead to financial strain. Here’s why enrolling in a health plan is non-negotiable:
✔ Financial Security – Avoid crippling medical debt by having coverage for hospital stays, surgeries, and prescriptions.
Preemptive Medical Care – Many plans cover free check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings to catch health issues early.
✔Adhering to Legal Standards – In some countries, having health insurance is mandatory to avoid penalties.
✔ Stress-Free Protection – Knowing you’re protected allows you to focus on recovery rather than bills.
Without insurance, a minor injury or chronic condition can quickly turn into a financial disaster. Enrolling in the right plan ensures you’re prepared for life’s uncertainties.
Everything You Need to Know About Health Plan Enrollment Periods

Not all enrollment opportunities are the same. Depending on your situation, you may qualify for different enrollment windows:
1. Healthcare Enrollment Timeframe (OEP)
Typically runs from November 1 to January 15 (dates may vary by state).
- Who Qualifies? Anyone can enroll, switch, or drop coverage.
- Key Tip: Missing this window means waiting another year unless you qualify for a Special Enrollment time.
2. Special Enrollment Period (SEP)
- Triggering Events:
- Marriage, divorce, or legal separation
- Birth or adoption of a child
- Loss of employer-sponsored coverage (e.g., job loss)
- Moving to a new state or county
- Deadline: Usually 60 days after the qualifying event.
3. Medicaid & CHIP Enrollment
- Year-Round Availability – Low-income families and individuals can apply anytime.
- Instant Coverage – Some states offer immediate approval for eligible applicants.
4. Medicare Enrollment
- Initial Enrollment Period (IEP): Starts 3 months before your 65th birthday and lasts 7 months.
- Annual Enrollment Period (AEP): October 15 – December 7 for changes to Medicare plans.
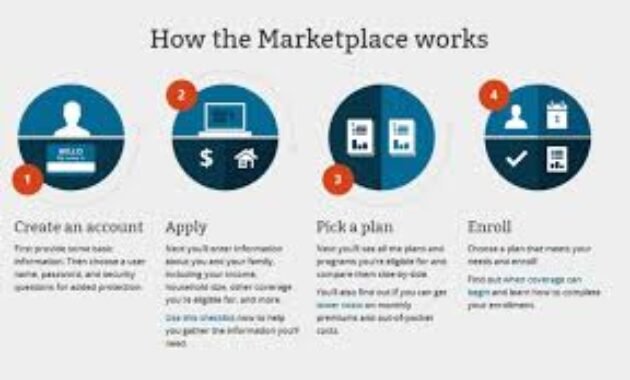
How to Enroll in Health Insurance: A Step-by-Step Process
Step 1: Examine Your Healthcare Expectations
Before choosing a plan, ask yourself:
- How often do I visit the doctor?
- Do I need specialist care or ongoing prescriptions?
Step 2: Compare Available Plans
- HMO (Health Maintenance Organization): Lower costs but restricted to in-network providers.
- PPO (Preferred Provider Organization): Offers greater flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, but typically comes with higher monthly premiums.
- EPO (Exclusive Provider Organization): Coverage is limited to in-network providers, except in cases of emergency.
- HDHP (High-Deductible Health Plan): Lower premiums but higher deductibles; pairs with HSAs.
Pro Tip: Use online comparison tools on healthcare.gov or private insurance websites.
Step 3: Get Your Documentation in Order
You’ll typically need:
- Proof of identity (driver’s license, passport)
- Social Security Number (or tax ID)
- Income documentation (e.g., paychecks, filed taxes)
- Current insurance details (if switching plans)
Step 4: Apply Through Your Preferred Method
- Online: Fastest method via healthcare.gov or state exchanges.
- Phone: Call the marketplace helpline for assistance.
- In-Person: Work with a licensed insurance agent or navigator.
- Mail: Some states allow paper applications.
Step 5: Review & Confirm Your Plan
- Double-check covered services, deductibles, and copays.
- Verify that your preferred doctors and hospitals are in-network.
- Confirm enrollment deadlines and first premium due date.
Step 6: Make Your First Payment
- Coverage only begins after the first premium is paid.
- Set up auto-pay to avoid accidental lapses.
Eligibility is determined by several key considerations:
Eligibility depends on several factors:
✅ Citizenship/Residency – U.S. citizens, lawful permanent residents, and certain visa holders qualify.
✅ Income Level – Subsidies (like ACA tax credits) are available for low-to-moderate-income households.
✅ Employment Status – Employer-sponsored plans vs. individual marketplace plans.
✅ Age – Children may qualify for CHIP, while seniors (65+) enroll in Medicare.
Note: Some states expanded Medicaid, allowing more people to qualify based on income alone.
Critical Deadlines You Can’t Afford to Miss
| Enrollment Type | Typical Deadline |
|---|---|
| ACA Open Enrollment | November 1 – January 15 |
| Medicare AEP | October 15 – December 7 |
| Employer-Sponsored | Varies (check with HR) |
| Special Enrollment | 60 days after qualifying event |
Late enrollment? You may face a coverage gap or penalties in some cases.
5 Common Enrollment Mistakes (And How to Avoid Them)
attached Until the Last Minute – Delaying can lead to rushed decisions or missed deadlines.
Not Comparing Plans – The cheapest premium may have high deductibles or limited coverage.
Providing Incorrect Information – Errors can delay approval or cause claim denials.
Ignoring Subsidies – Many qualify for discounts but don’t apply due to lack of awareness.
Skipping the Fine Print – Always review exclusions (e.g., certain medications or treatments).
Final Thoughts: Secure Your Health & Financial Future
Enrolling in health insurance is one of the most important decisions you’ll make for your well-being. By understanding the process, preparing documents in advance, and choosing the right plan, you can avoid unnecessary stress and financial strain.
Need Help?
- Visit Healthcare.gov for official guidance.
- Consult a licensed insurance agent for personalized advice.
- Use free enrollment assisters if you’re unsure about the process.




